Plastic vs. Glass Reagent Bottles: Advantages and Disadvantages
When storing and transporting reagents, whether for laboratory use or industrial applications, container selection is critical. There are two main types of commonly used reagent bottles: plastic (PP and HDPE) and glass. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and understanding these can help you make an informed decision when choosing the right container for your specific needs.
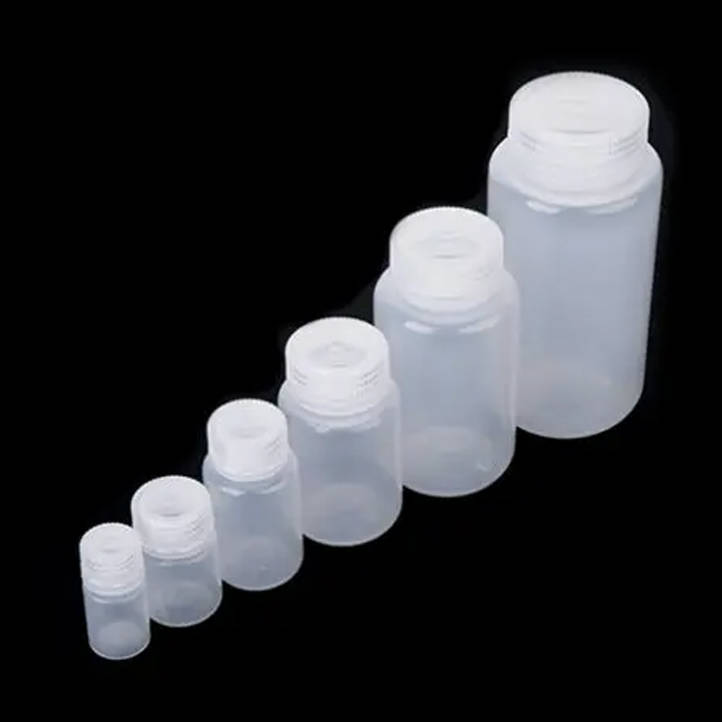
Advantages of plastic reagent bottles
Plastic reagent bottles, especially those made from polypropylene (PP) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE), offer several advantages over glass reagent bottles. One of the main advantages is durability. Plastic bottles are significantly less likely to crack or break, making them suitable for transport and handling in busy laboratory and industrial environments. This reduces the risk of accidents and potential exposure to harmful substances.
Additionally, plastic reagent bottles are generally lighter in weight than glass bottles, making them easier to handle and transport. This is particularly useful when handling large quantities of reagents or transporting reagents over long distances. Additionally, the lightweight nature of plastic bottles saves on shipping and handling costs.
Another advantage of plastic reagent bottles is their resistance to many chemicals and solvents. Both PP and HDPE are known for their excellent chemical resistance, which makes them suitable for use with a wide range of agents and substances. This prevents chemicals from leaching into the reagents, ensuring their integrity and maintaining the purity of the stored substances.
In addition, plastic reagent bottles often come with screw caps or other closures that provide a secure seal and help prevent leakage and contamination. This is especially important for sensitive reagents that require sealed storage conditions.
Disadvantages of plastic reagent bottles
Although plastic reagent bottles have many advantages, there are also some disadvantages. One of the main disadvantages is that they may absorb or adsorb certain chemicals. While PP and HDPE are generally resistant to most solvents, some substances may be absorbed by the plastic, resulting in possible contamination of the reagents. This can be a problem for some applications where purity is critical.
Additionally, plastic reagent bottles may not be as visually appealing as glass bottles. This can be a consideration for laboratories or industries where appearance and aesthetics are important.
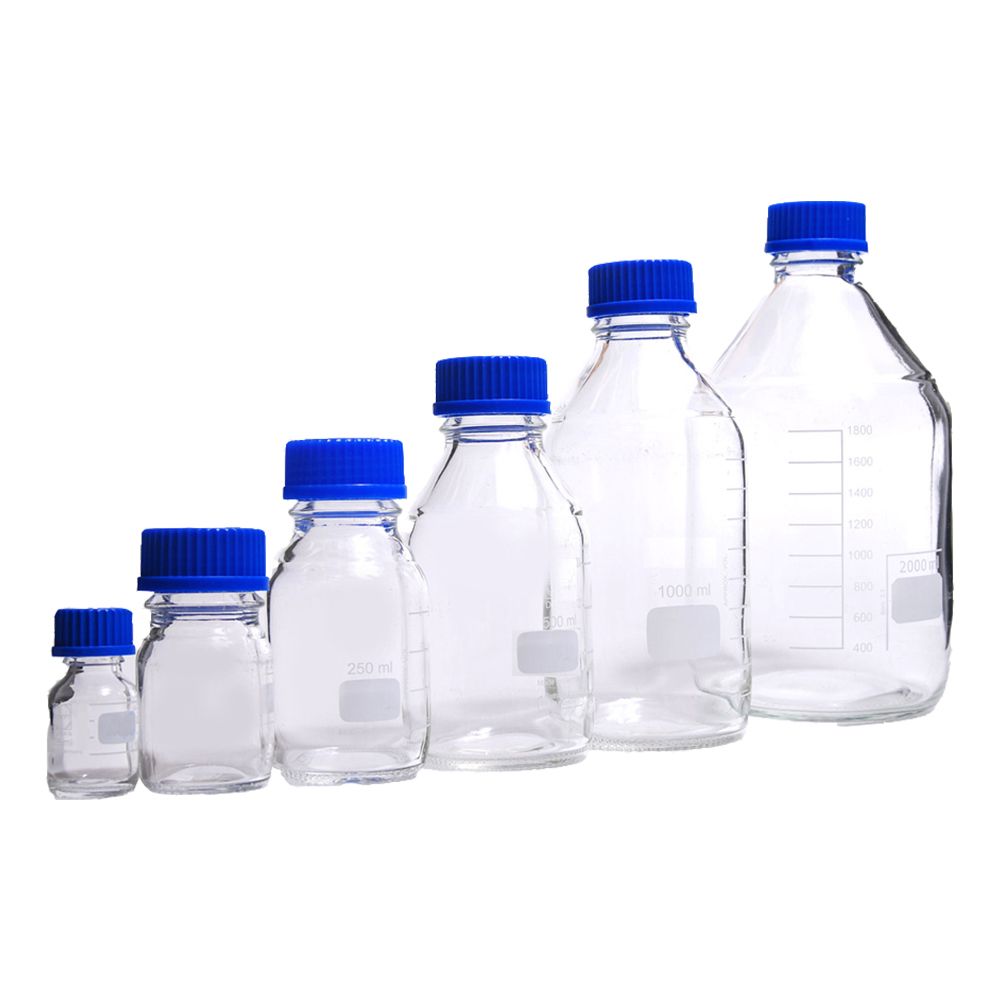
Advantages of glass reagent bottles
Glass reagent bottles have been the traditional choice for storing and transporting reagents for many years and offer a variety of advantages. One of the main advantages of glass bottles is their inertness. Unlike plastic, glass is non-reactive and does not absorb or adsorb chemicals, making it ideal for storing a wide range of reagents without the risk of contamination.
Another advantage of glass reagent bottles is their transparency. The glass allows for easy visual inspection of the contents, making it easy to monitor the condition of the reagents or check for any signs of contamination. This is especially important with sensitive reagents or when precise measurements are required.
Additionally, glass reagent bottles are generally better for long-term storage because they are less likely to degrade or change over time than plastic containers. This is critical for reagents that require extended storage life.
Disadvantages of glass reagent bottles
Despite these advantages, glass reagent bottles also have some disadvantages. One of the most significant disadvantages is their fragility. Glass bottles break easily, especially if dropped or mishandled. This may pose a safety risk and result in the loss of valuable reagents.
Additionally, glass bottles are generally heavier than plastic bottles, making them more cumbersome to handle and transport. This can be a consideration for applications where weight is a concern or where large amounts of reagents need to be moved.
In addition, glass bottles may be more susceptible to chemical attack by certain substances, especially strong acids or alkalis. Over time, this can cause the glass to degrade, potentially compromising the integrity of the stored reagents.
in conclusion
Both plastic and glass reagent bottles have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two will depend on the specific requirements of your application. When selecting a reagent bottle, it is important to consider factors such as durability, chemical resistance, clarity, and weight, as well as the specific reagents being stored.
Plastic reagent bottles in general, especially those made from PP and HDPE, are ideal for applications where durability, chemical resistance, and lightweight handling are critical. Glass reagent bottles, on the other hand, excel in applications where inertness, transparency, and long-term storage are key considerations.
Ultimately, the choice between plastic and glass reagent bottles will depend on your specific needs and the characteristics of the reagents being stored. By carefully weighing the pros and cons of each type of bottle, you can make an informed choice that best suits your requirements.
Contact Suzhou Ace Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd. today to learn more about our range of plastic reagent bottles and how they can benefit your laboratory operations.
Post time: Dec-06-2023